This technology is based on quarter wave transformation line.
The coaxial shorting stub applied for this purpose is short circuited at its end and its length is matched to the mid-band frequency of the operation band.It threby forms a band-pass filter.
Since lightning interference have a low frequency spectrum the shorting stub act as a short circuit, conducting the current to ground.
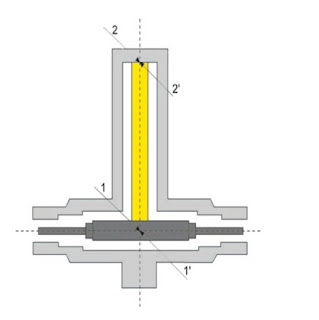
In regular operation, the RF signal reaches the entry of the shorting stub (shown here as point 1).
It then runs along the shorting stub up to the short (point 2). This corresponds to a 90° phase shift.
At the short, the signal is reflected (point 2') –a sudden phase shift of 180° is created – and flows back to the start of the shorting stub (point 1'), where it arrives after another 90° phase shift.
The coaxial shorting stub applied for this purpose is short circuited at its end and its length is matched to the mid-band frequency of the operation band.It threby forms a band-pass filter.
Since lightning interference have a low frequency spectrum the shorting stub act as a short circuit, conducting the current to ground.
In regular operation, the RF signal reaches the entry of the shorting stub (shown here as point 1).
It then runs along the shorting stub up to the short (point 2). This corresponds to a 90° phase shift.
At the short, the signal is reflected (point 2') –a sudden phase shift of 180° is created – and flows back to the start of the shorting stub (point 1'), where it arrives after another 90° phase shift.
As a result, the reflected signal is again in phase with the arriving signal. Therefore, the RF signal does not detect the short.
To go back to main page please click here